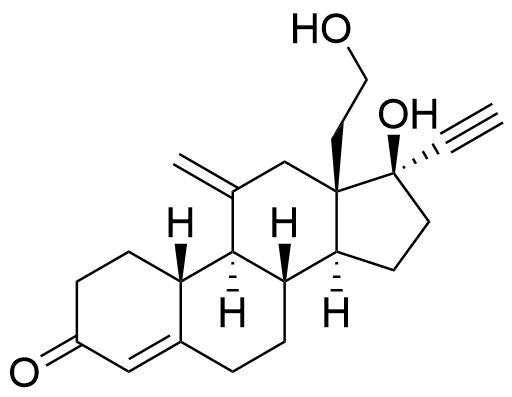
Etonogestrel
Etonogestrel (ENG) is a synthetic progestin derived from testosterone and used in hormonal contraceptives. Etonogestrel is primarily used in implants and vaginal rings, while its prodrug desogestrel (DSG) is primarily used in oral contraceptives.
Tags
Approvals
WHO Essential Medicine WHO Prequalification US FDA-ApprovedRelated Compounds
Desogestrel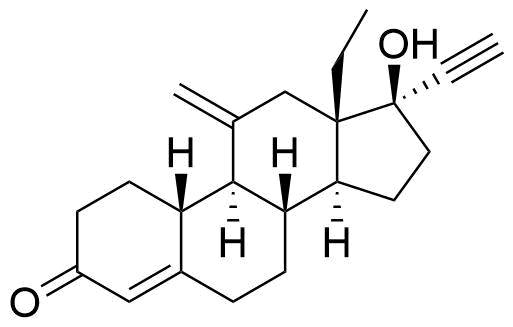
Identifiers
Abbreviation
ENG, ETN, KDG or 3-KDG
References
Names
- 3-ketodesogestrel
- 3-oxodesogestrel
References
CASRN
54048-10-1
References
PubChem CID
- 122130103 (as 3-Keto Desogestrel)
- 6917715 (as Etonogestrel)
- 21729469 (unnamed)
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.053.561
- EC / List #: 258-936-2
IUPHAR/BPS
7590
DrugBank Accession Number
DB00294
References
- DrugBank: Etonogestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
UNII
304GTH6RNH
KEGG Entry Number
D04104
Wikipedia Entry Name
Etonogestrel
ChEBI ID
CHEBI:50777
ChEMBL ID
CHEMBL1531
ChemSpider ID
5292944
NIST
(17α)-13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-11-methylene-18,19-dinorpregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one
ATC Code(s)
Physical & Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula
C22H28O2
References
Molecular Weight
324.46 g/mol
References
logP
3.4
Specific Optical Rotation
+85.0 to +95.0° dried, 10 mg/mL in CH2Cl2
References
- United States Pharmacopoeia 2014 Etonogestrel (View all citations for this reference)
Toxicology
GHS Hazard Code(s)
| Class | Category | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenicity | 2 | H351 | Suspected of causing cancer if inhaled |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1B | H360 | May damage fertility or the unborn child |
| Acute Dermal Toxicity | 4 | H312 | Harmful in contact with skin |
| Acute Inhalation Toxicity | 4 | H332 | Harmful if inhaled |
Side Effects
Vaginal inflammation, headache, breast pain, URI, haemorrhage, abdominal pain, pharyngitis, Leukorrhea, weight gain, flu-like symptoms, acne, dizziness, dysmenorrhoea, back pain, nausea
References
- Implanon. SIDER: Side Effect Resource [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- AHFS Drug Information 2017 section 68:12 Contraceptives. An American Society of Health-System Pharmacists reference. (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
Carcinogenicity
No treatment-related tumorigenic effects seen from administration of desogestrel only.
Genotoxicity
Not associated with point mutations in the in vitro Ames test and to chromosomal aberrations in a micronucleus test in female rats.
Biochemistry & Pharmacology
Progesterone Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
Androgen Receptor Activity
Listed as "weak" (Jordan) and "active" (Ruan, Lello) agonist.
References
- Jordan A. Toxicology of progestogens of implantable contraceptives for women. Contraception. 2002; 65:3-8. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Estrogen Receptor Activity
Antagonist
References
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- Jordan A. Toxicology of progestogens of implantable contraceptives for women. Contraception. 2002; 65:3-8. (View all citations for this reference)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity
Reports vary: "weak" (Kuhl), "active" (Bartsch), "not active" (Ruan, Lello)
References
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Bartsch, V., Gynaecological uses of dienogest alone and in combination with oestrogens. Journal of Medical Drug Reviews 2015, 5, 1-31. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Target Pathways
Bioavailability
- Oral: 70-75%
- Subdermal implant: 100%
References
- Desogestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Timmer, C. J.; Srivastava, N.; Dieben, T. O. M.; Cohen, A. F. Bioavailability and Bioequivalence of Etonogestrel from Two Oral Formulations of Desogestrel: Cerazette (R) and Liseta (R). Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 1999, 24 (4), 335–343. (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
- Primiero, F. M.; Lombardi, G.; Bianchi, P. Implanon: New Concepts in Long-Acting Contraception. In 2nd International Congress on New Technologies in Reproductive Medicine, Neonatalogy and Gynecology; Cosmi, EV, Ed.; 1999; pp 281–286. (View all citations for this reference)
Elimination Half-Life (t1/2)
12-24 h, 30 h, 38 +/- 20 h
References
- Desogestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
Serum Protein Binding
95.5-99% bound. 66% to albumin, 32% to SHBG.
References
- Desogestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- Nilsson, B.; von Schoultz, B., Binding of levonorgestrel, norethisterone and desogestrel to human sex hormone binding globulin and influence on free testosterone levels. Gynecol Obstet Invest 1989, 27 (3), 151-4. (View all citations for this reference)
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
- Rebar, R. W.; Zeserson, K., CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NEW PROGESTOGENS IN COMBINATION ORAL-CONTRACEPTIVES. Contraception 1991, 44 (1), 1-10. (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolism
CYP3A4
Excretion
Excreted free or as conjugates, primarily via urine (60%) and feces (35%). Small amounts excreted in the breast milk; as a result, 0.01-0.05 ug per kg body weight per day may be ingested by the child.
References
- Desogestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- PubChem: Etonogestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
Apparent Volume of Distribution
201 L
Cmax
- 640 pg/mL from oral administration of 75 μg desogestrel
- 4273 +/- 830 ng/L from 30 μg ethinyl estradiol/150 μg desogestrel oral pill
- 1716 +/- 445 ng/L from etonogestrel vaginal ring
- 813 pg/mL from subdermal implant
Tmax
- Oral: 1.5 h; 2-3 h
- Subdermal implant: 4 days
References
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Desogestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- Grandi, G.; Cagnacci, A.; Volpe, A. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Desogestrel as a Female Contraceptive. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10 (1), 1–10. (View all citations for this reference)
Clearance
Subdermal implant: 7.5 L/h
Enzyme Interactions
CYP2C19, CYP3A4: inhibitor
References
- Laine, K.; Yasar, U.; Widen, J.; Tybring, G. A Screening Study on the Liability of Eight Different Female Sex Steroids to Inhibit CYP2C9, 2C19 and 3A4 Activities in Human Liver Microsomes. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93 (2), 77–81. (View all citations for this reference)
Minimum Contraceptive Threshold
Possibly > 90 pg/mL
Indications
For use as a female contraceptive (depot).
Metabolites
Name
Structure
Notes
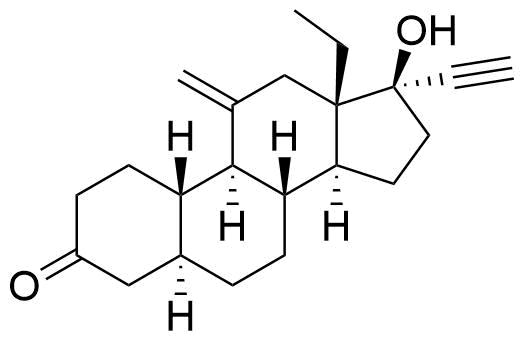
Lower Progesterone Receptor and Estrogen Receptor activity than etonogestrel.
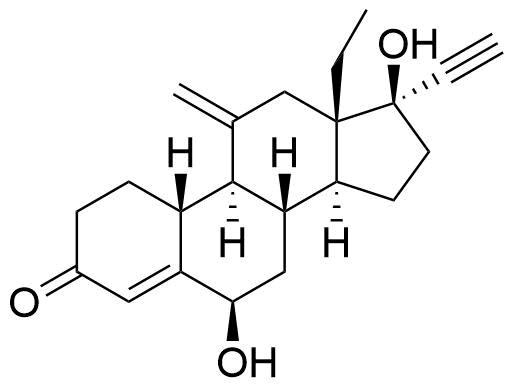
Primary metabolite from human hepatic microsome metabolism. Likely formed by CYP3A4, as this enzyme is responsible for 6β-hydroxylation pathways in other steroids.