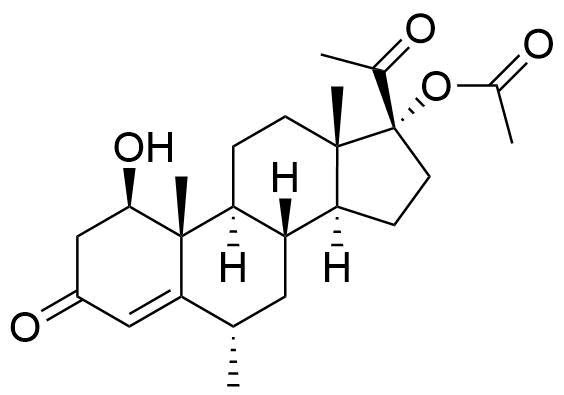
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
Medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) is a synthetic progestogen used in hormonal contraceptives, as a component in hormone replacement therapy, and in treatment for various other medical issues. It is widely known by the brand name Depo-Provera.
Tags
Approvals
WHO Essential Medicine WHO Prequalification US FDA-Approved
Identifiers
Abbreviation
MPA
References
Names
- 6α-methyl-17α-acetoxyprogesterone
- 6α-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate
References
CASRN
71-58-9
References
PubChem CID
6279
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.000.689
- EC / List #: 200-757-9
IUPHAR/BPS
2879
DrugBank Accession Number
DB00603
References
- DrugBank: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate.
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
UNII
C2QI4IOI2G
KEGG Entry Number
C08150
Wikipedia Entry Name
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
ChEBI ID
CHEBI:6716
ChEMBL ID
CHEMBL717
ChemSpider ID
6043
NIST
Medroxyprogesterone Acetate
ATC Code(s)
Physical & Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula
C24H34O4
References
Molecular Weight
386.5 g/mol
References
Appearance
White or almost white crystalline powder, odorless.
References
- British Pharmacopoeia 2014: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate API (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Melting Point
PubChem: 214.5° C
IARC: 207-209 °C
References
- PubChem: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water. Slightly soluble in diethyl ether. Freely soluble in chloroform and dichloromethane. Soluble in acetone and dioxane. Sparingly soluble in ethanol and methanol.
References
- British Pharmacopoeia 2014: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate API (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
logP
3.5
Specific Optical Rotation
+47 to +53 (dried substance 0.250 g in acetone diluted to 25 mL).
+45 to +51 deg, 10 mg per mL in dioxane.
+61° in chloroform
References
- British Pharmacopoeia 2014: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate API (View all citations for this reference)
- United States Pharmacopoeia 36 (2013): Medroxyprogesterone Acetate. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Storage Conditions
"Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store at 25° C, excursions permitted between 15° C and 30° C."
References
- United States Pharmacopoeia 36 (2013): Medroxyprogesterone Acetate. (View all citations for this reference)
Toxicology
GHS Hazard Code(s)
| Class | Category | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carcinogenicity | 2 | H351 | Suspected of causing cancer if inhaled |
| Acute Oral Toxicity | 4 | H302 | Harmful if swallowed |
| Acute Dermal Toxicity | 4 | H312 | Harmful in contact with skin |
| Acute Inhalation Toxicity | 4 | H332 | Harmful if inhaled |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1B | H360 | May damage fertility or the unborn child |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1A | H360 | May damage fertility or the unborn child |
| Reproductive Toxicity, Effects On or Via Lactation | H362 | May cause harm to breast-fed children |
Side Effects
Increases risk of breast cancer and coronary heart disease in hormone replacement therapy (HRT) users by disturbing normal signaling of natural androgens which play a protective role against breast cancer. Negative effects on bone density due to glucocorticoid activity. Possible weight gain, increased blood pressure, and cardiovascular complications due to no or very weak antimineralocorticoid activity. As an injectable contraceptive, associated with increased HIV acquisition. Nervousness, abdominal distress, headache, metrorrhagia, amenorrhoea, libido decreased, dizziness, weight increased, asthenia, injection site reaction.
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Side Effects Database, Medroxyprogesterone Acetate. (View all citations for this reference)
Carcinogenicity
There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for carcinogenicity of MPA.
Mutagenicity
Non-mutagenic in Ames test, DNA damage/alkaline elution assay, and micronucleus test.
LD50
LD50 dog oral: > 5 g/kg
LD50 mouse intraperitoneal: > 1.5 g/kg
LD50 mouse oral: > 16 g/kg
LD50 mouse subcutaneous: > 1.5 g/kg
LD50 mouse intravenous, single dose: 376 mg/kg
LD50 rat intraperitoneal: > 0.9 g/kg
LD50 rat oral: > 6.4 g/kg
LD50 rat subcutaneous: > 0.9 g/kg
LD50rat intravenous, single dose: ~100 mg/kg
TDLo
human women intravenous: 10-21 mg/kg
Biochemistry & Pharmacology
Progesterone Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
Androgen Receptor Activity
Reported as weakly effective to effective agonist.
References
- Sitruk-Ware, R.; Small, M.; Kumar, N.; Tsong, Y.-Y.; Sundaram, K.; Jackanicz, T., Nestorone®: clinical applications for contraception and HRT. Steroids 2003, 68 (10-13), 907-913. (View all citations for this reference)
- Sitruk-Ware, R., Pharmacological profile of progestins. Maturitas 2004, 47, 277-283. (View all citations for this reference)
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Estrogen Receptor Activity
Antagonist
References
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Mueck, A. O.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Nomegestrol acetate, a novel progestogen for oral contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (6), 531-539. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Bioavailability
Near 100%
References
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
Elimination Half-Life (t1/2)
32-44 h (oral administration)
Serum Protein Binding
88% bound to serum albumin, no binding to SHBG or CBG
References
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolism
CYP3A4. No hepatic first pass effects after oral intake.
References
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Nanda, K.; Stuart, G. S.; Robinson, J.; Gray, A. L.; Tepper, N. K.; Gaffield, M. E. Drug Interactions between Hormonal Contraceptives and Antiretrovirals. AIDS 2017, 31 (7), 917–952. (View all citations for this reference)
Excretion
Most metabolites excreted in the urine as glucuronide conjugates with only minor amounts excreted as sulfates. Detectable amounts have been found in milk.
Tmax
2-4 h
Enzyme Interactions
- Competitive inhibitor of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/Δ5-4 isomerase II (3β-HSDII), which is essential for the biosynthesis of sex steroids and corticosteroids.
- CYP3A4: substrate, inducer
- CYP2C8, CYP2C9: inhibitor
References
- Wikipedia: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate (View all citations for this reference)
- PubChem: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate. (View all citations for this reference)
- Laine, K.; Yasar, U.; Widen, J.; Tybring, G. A Screening Study on the Liability of Eight Different Female Sex Steroids to Inhibit CYP2C9, 2C19 and 3A4 Activities in Human Liver Microsomes. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2003, 93 (2), 77–81. (View all citations for this reference)
- Medroxyprogesterone. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
Indications
Used as a contraceptive and to treat secondary amenorrhea, abnormal uterine bleeding, pain associated with endometriosis, endometrial and renal cell carcinomas, paraphilia in males, GnRH-dependent forms of precocious puberty, as well as to prevent endometrial changes associated with estrogens.
Metabolites
Name
Structure
Notes
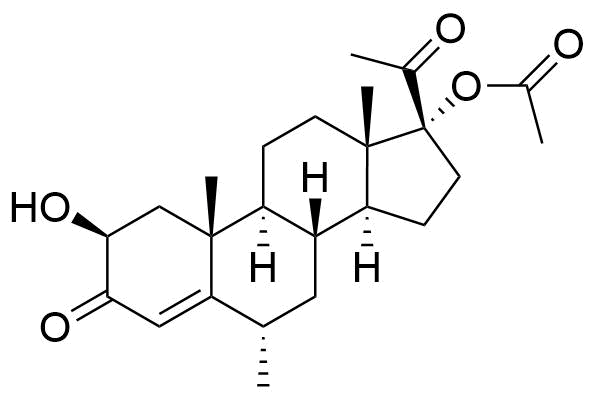
Proposed structure of an MPA metabolite observed in MPA incubation with human liver microsomes.
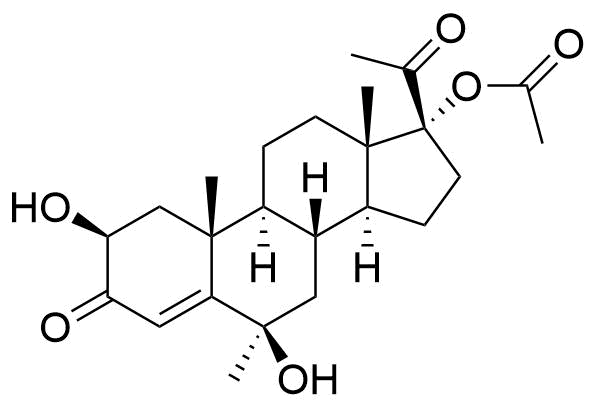
Proposed structure of an MPA metabolite observed in MPA incubation with human liver microsomes.
Very little is known about the metabolism of MPA. Other metabolites may result from modifications at C17 and C21, and/or ring A reduction.
Impurities
Name
Structure
CASRN
Other Names & Identifiers
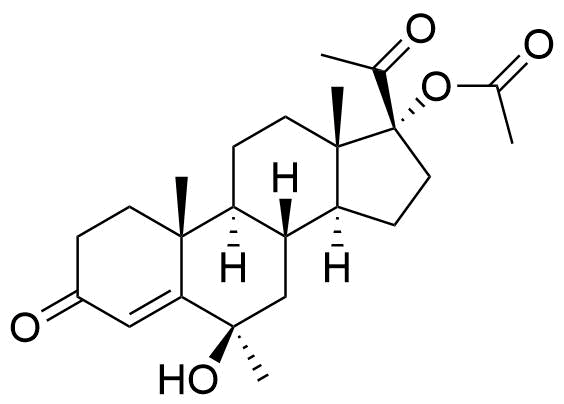
- BP MPA Impurity A
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Injection Impurity A
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Tablets Impurity A
- 17α-acetoxy-6β-hydroxy-6α-methyl-pregn-4-en-3,20-dione
- 6β-hydroxy-6-methyl-3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-17-yl acetate
520-85-4
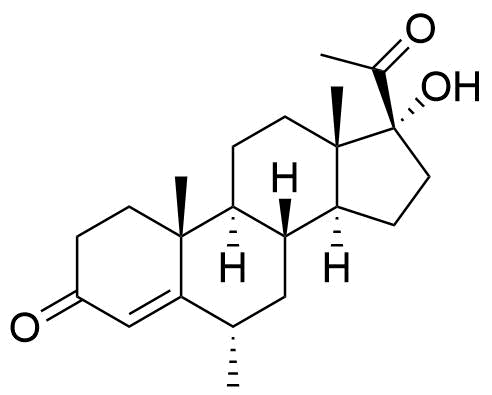
- BP MPA Impurity B
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Injection Impurity B
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Tablets Impurity B
- 17-hydroxy-6α-methylpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
- BP MPA Impurity C
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Injection Impurity C
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Tablets Impurity C
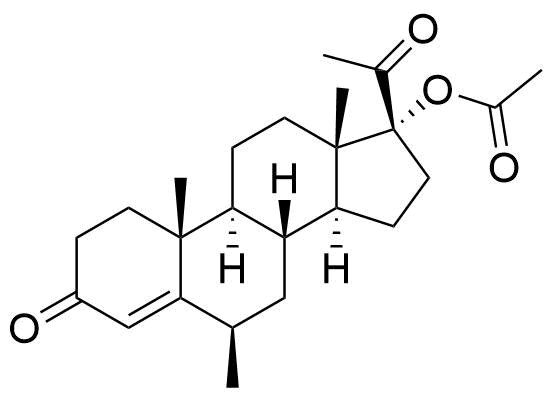
2242-65-1
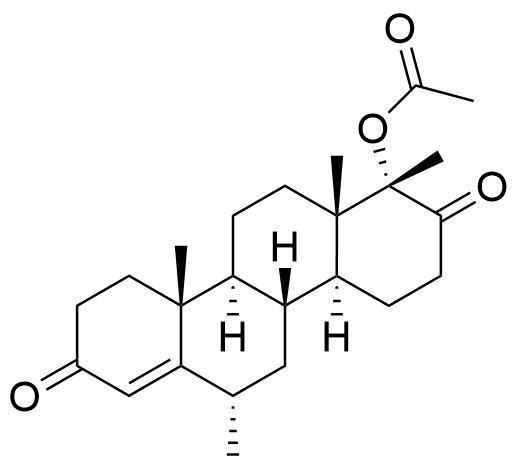
- BP MPA Impurity D
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Injection Impurity D
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Tablets Impurity D
- BP Megestrol Acetate Impurity F
- 6β-methyl-17α-hydroxyprogesteron-17-acetate
32634-95-0
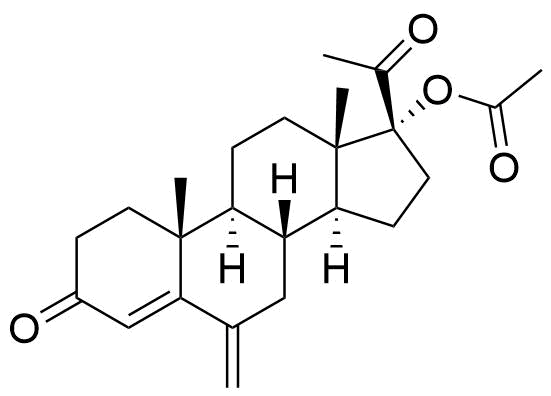
- BP MPA Impurity E
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Injection Impurity E
- BP Medroxyprogesterone Tablets Impurity E
- 17-acetoxy-6-methylene-4-pregnene-3,20-dione
- 6-methylidene-3,20-dioxopregn-4-en-17-yl acetate
US FDA-Approved Products
Name
Formulation
Status
ANDA #
Injectable
Prescription
077334
Injectable
Prescription
077235
Discontinued
088484
Discontinued
078711
Prescription
076553
WHO Essential Medicines
Name
Formulation
Tablet
Classified as 18.7 Progestogens
Intramuscular injection
MEDROXYPROGESTERONE ACETATE: 104 mg/0.65mL in pre-filled syringe or single-dose injection delivery system
Subcutaneous injection
MEDROXYPROGESTERONE ACETATE: 25 mg
Injection