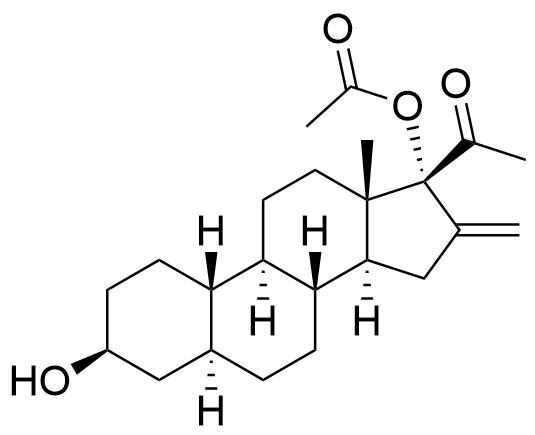
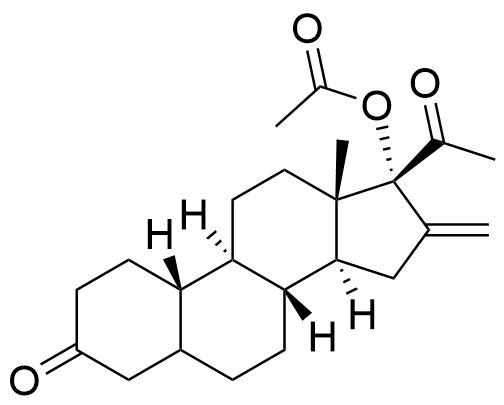
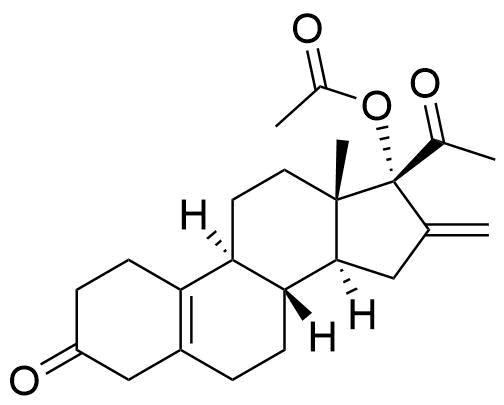
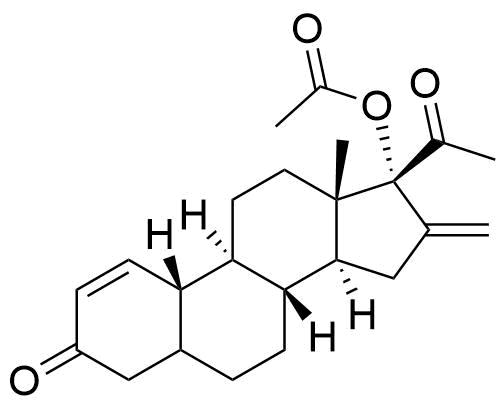
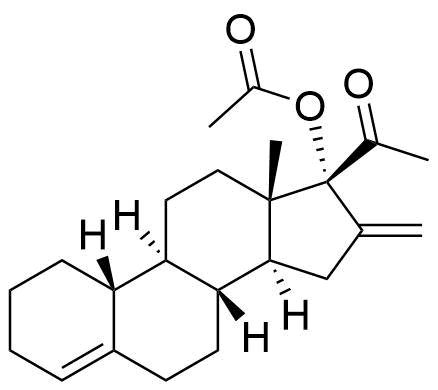
Nestorone
Nestorone (NES) is a synthetic progestogen designed with high specificity for the progesterone receptor. It is being investigated for use in hormonal contraceptives but is currently not used in any approved products internationally.
Tags
Identifiers
Abbreviation
NES
References
Names
- Nestoron
- segesterone acetate
- elcometrine
- ST1435
- ST-1435
- 16-methylene-17α-acetoxy-19-nor-4-pregnene-3,20-dione acetate
- 17-hydroxy-16-methylene-19-norpregn-4-ene-3,20-dione acetate
CASRN
7759-35-5
References
PubChem CID
108059
UNII
9AMX4Q13CC
Wikipedia Entry Name
Segesterone Acetate
ChEBI ID
CHEBI:135563
ChEMBL ID
CHEMBL3707377
ChemSpider ID
97161
Physical & Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula
C23H30O4
References
Molecular Weight
370.482 g/mol
References
Melting Point
178-179° C
Solubility
Soluble in DMSO, 5 mg/mL
Specific Optical Rotation
-103.3 °, 1g/100 mL CHCl3
Toxicology
Genotoxicity
3 tests showed no gene mutations and did not affect chromosomal integrity
References
- Jordan A. Toxicology of progestogens of implantable contraceptives for women. Contraception. 2002; 65:3-8. (View all citations for this reference)
Safety Profile Overview
Similar safety profile to progestogens found in approved oral contraceptives; no significant or unusual toxicities.
References
- Jordan A. Toxicology of progestogens of implantable contraceptives for women. Contraception. 2002; 65:3-8. (View all citations for this reference)
Biochemistry & Pharmacology
Progesterone Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
- Kumar, N.; Fagart, J.; Liere, P.; Mitchell, S. J.; Knibb, A. R.; Petit-Topin, I.; Rame, M.; El-Etr, M.; Schumacher, M.; Lambert, J. J.; Rafestin-Oblin, M. E.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Nestorone(R) as a Novel Progestin for Nonoral Contraception: Structure-Activity Relationships and Brain Metabolism Studies. Endocrinology 2017, 158 (1), 170-182. (View all citations for this reference)
Androgen Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Fagart, J.; Liere, P.; Mitchell, S. J.; Knibb, A. R.; Petit-Topin, I.; Rame, M.; El-Etr, M.; Schumacher, M.; Lambert, J. J.; Rafestin-Oblin, M. E.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Nestorone(R) as a Novel Progestin for Nonoral Contraception: Structure-Activity Relationships and Brain Metabolism Studies. Endocrinology 2017, 158 (1), 170-182. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Koide, S. S.; Tsong, Y.; Sundaram, K., Nestorone: a progestin with a unique pharmacological profile. Steroids 2000, 65 (10-11), 629-36. (View all citations for this reference)
- Sitruk-Ware, R.; Small, M.; Kumar, N.; Tsong, Y.-Y.; Sundaram, K.; Jackanicz, T., Nestorone®: clinical applications for contraception and HRT. Steroids 2003, 68 (10-13), 907-913. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Estrogen Receptor Activity
Antagonist
References
- Kumar, N.; Fagart, J.; Liere, P.; Mitchell, S. J.; Knibb, A. R.; Petit-Topin, I.; Rame, M.; El-Etr, M.; Schumacher, M.; Lambert, J. J.; Rafestin-Oblin, M. E.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Nestorone(R) as a Novel Progestin for Nonoral Contraception: Structure-Activity Relationships and Brain Metabolism Studies. Endocrinology 2017, 158 (1), 170-182. (View all citations for this reference)
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
- Sitruk-Ware, R.; Small, M.; Kumar, N.; Tsong, Y.-Y.; Sundaram, K.; Jackanicz, T., Nestorone®: clinical applications for contraception and HRT. Steroids 2003, 68 (10-13), 907-913. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Koide, S. S.; Tsong, Y.; Sundaram, K., Nestorone: a progestin with a unique pharmacological profile. Steroids 2000, 65 (10-11), 629-36. (View all citations for this reference)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity
Binds to GR but does not show activity in in vivo assays
References
- Sitruk-Ware, R., Pharmacological profile of progestins. Maturitas 2004, 47, 277-283. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Koide, S. S.; Tsong, Y.; Sundaram, K., Nestorone: a progestin with a unique pharmacological profile. Steroids 2000, 65 (10-11), 629-36. (View all citations for this reference)
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Elimination Half-Life (t1/2)
26.8 h
References
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
Serum Protein Binding
Binds to albumin. Does not bind to SHBG.
References
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
- Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams; Victoria F. Roche; S. William Zito (24 January 2012). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 1403. ISBN 978-1-60913-345-0. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Koide, S. S.; Tsong, Y.; Sundaram, K., Nestorone: a progestin with a unique pharmacological profile. Steroids 2000, 65 (10-11), 629-36. (View all citations for this reference)
- Sitruk-Ware, R.; Small, M.; Kumar, N.; Tsong, Y.-Y.; Sundaram, K.; Jackanicz, T., Nestorone®: clinical applications for contraception and HRT. Steroids 2003, 68 (10-13), 907-913. (View all citations for this reference)
Enzyme Interactions
Inhibits 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 (HSD3B2) and reduces the biosynthesis of several endogenous steroids.
References
- Toit, R. L. D.; Perkins, M. S.; Snoep, J. L.; Storbeck, K. H.; Africander, D., Fourth-generation progestins inhibit 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 and modulate the biosynthesis of endogenous steroids. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1-24. (View all citations for this reference)
Route of Administration
Parenteral. Orally inactive.
References
- Su, Y.; Lian, Q. Q.; Ge, R. S., Contraceptives with novel benefits. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2012, 21 (1), 83-90. (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolites
Name
Structure
Notes
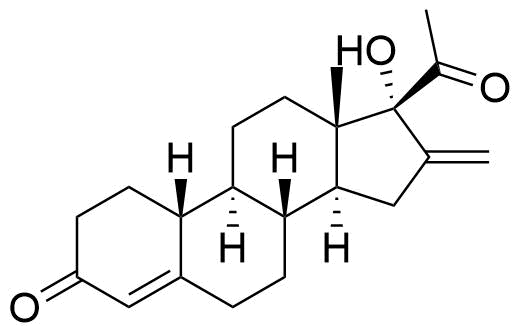
Minor metabolite. Also a degradant (see Nestorone Impurity 13). HPLC and MS.
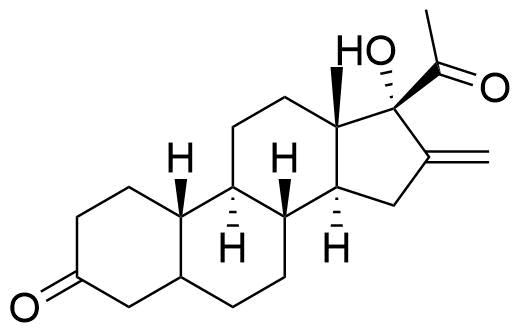
Major metabolite as identified by Prasad et al. (19 total metabolites found but only 2 identified). HPLC and MS.
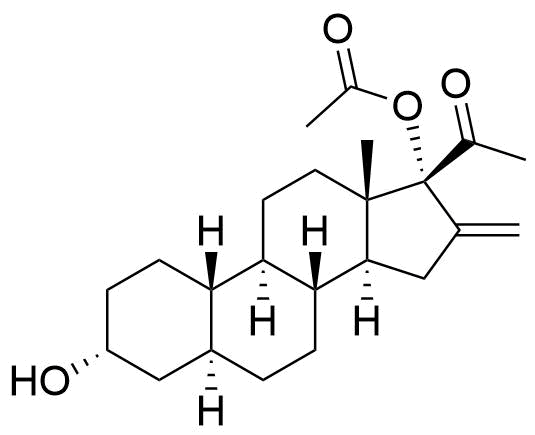
120 times less potent PR activity than Nestorone in human PR (hPR) transactivation assay (EC50 = 24 pM for NES vs. 2850 pM for metabolite). GC/MS-MS.
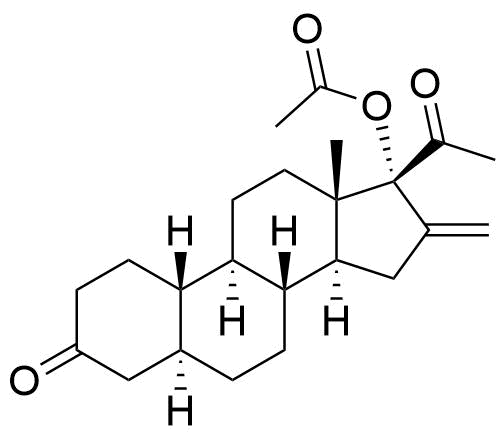
Identified in vitro, detected in plasma and brain of mice. Most abundant metabolite in mouse brain at 30 min post administration. 17 times less potent PR activity than nestorone in human PR transactivation assay (EC50 = 410 pM vs. EC50 of Nestorone = 24 pM).
Impurities
Name
Structure
CASRN
Other Names & Identifiers
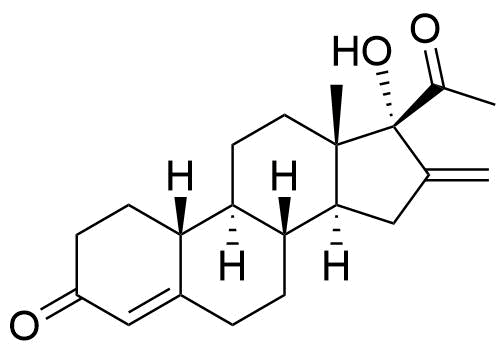
7690-08-6
- 16-methylene-17α-hydroxy-19-nor-pregn-4-ene-3,20-dione
- 17α-hydroxy-16-methylene-19-norprogesterone
- 17α-deacetylnestorone