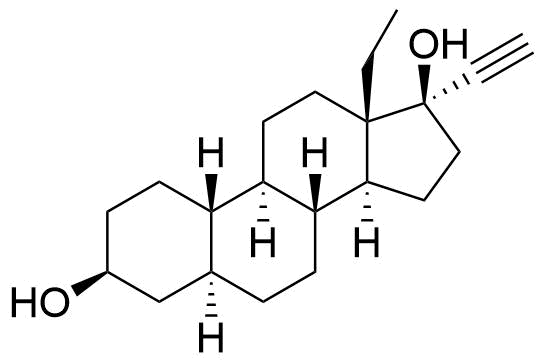
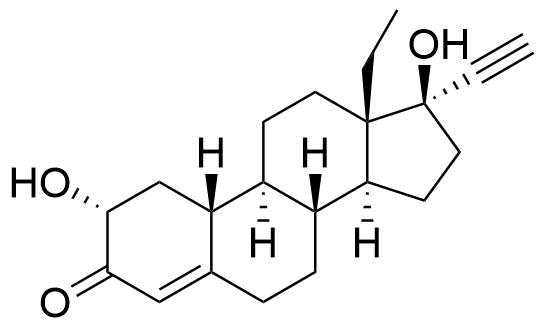
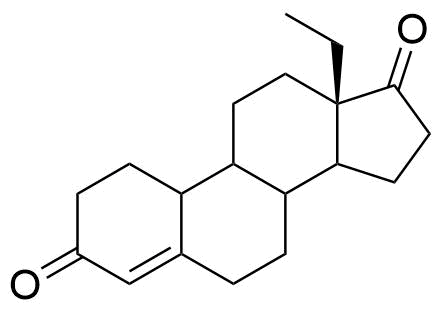
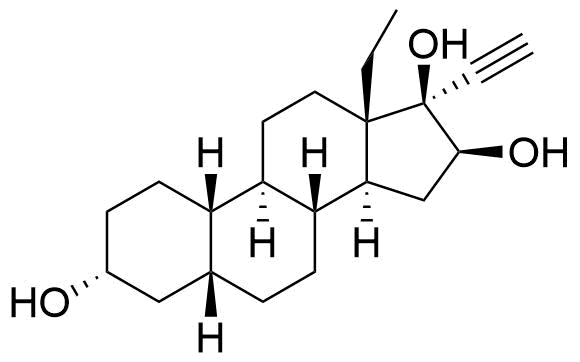
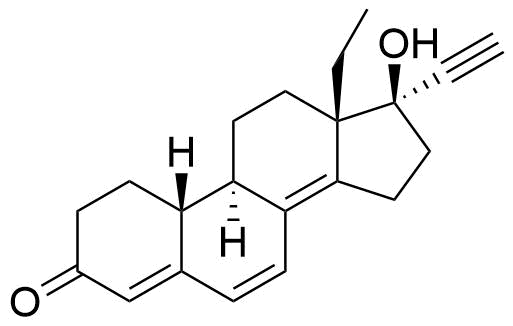
Levonorgestrel
Levonorgestrel (LNG) is a synthetic progestational hormone used in hormonal contraceptives and as a component in hormone replacement therapy. It is the biologically active form of the racemic mixture norgestrel.
Tags
Approvals
WHO Essential Medicine WHO Prequalification US FDA-ApprovedRelated Compounds
Norgestrel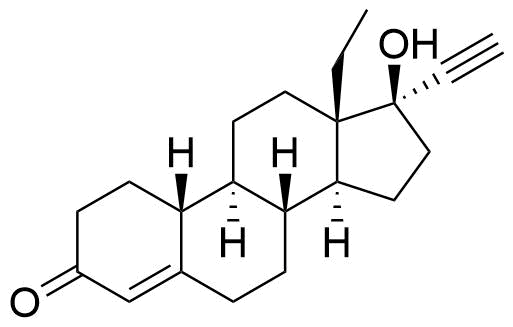
Identifiers
Abbreviation
LNG
References
Names
- USAN, INN: Levonorgestrel
- 18-methylnorethisterone
- 17α-ethynyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone
- 17α-ethynyl-18-methylestr-4-en-17β-ol-3-one
References
CASRN
797-63-7
References
PubChem CID
13109
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.011.227
- EC/List #: 212-349-8
IUPHAR/BPS
2881
DrugBank Accession Number
DB00367
References
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
UNII
5W7SIA7YZW
Reaxys ID
6067808
KEGG Entry Number
D00950
Wikipedia Entry Name
Levonorgestrel
ChEBI ID
CHEBI:6443
ChEMBL ID
CHEMBL1389
ChemSpider ID
12560
ATC Code(s)
References
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Physical & Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula
C21H28O2
References
Molecular Weight
312.45 g/mol
References
Appearance
White, crystalline powder
Melting Point
USP: 232-239° C, but the range between start and end of melting does not exceed 4° C
IARC: 235-237 °C
References
- US Pharmacopoeia 40 (2017): Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Solubility
Slightly soluble in ethanol (1 in 120), chloroform (1 in 15), diethyl ether (1 in 400) and dioxane
References
- Levonorgestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- PubChem: Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
logP
3.48
Specific Optical Rotation
USP: Between -30 and -35°, 20 mg/mL in chloroform
-32.4 °C in chloroform
References
- US Pharmacopoeia 40 (2017): Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Vapor Pressure
3.92 x 10-10 mm Hg at 25° C (estimated)
Density
1.197 g/cm3
Storage Conditions
20 to 25° C (68 to 77° F). Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers.
References
- US Pharmacopoeia 40 (2017): Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
Toxicology
GHS Hazard Code(s)
| Class | Category | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Dermal Toxicity | 4 | H312 | Harmful in contact with skin |
| Acute Inhalation Toxicity | 4 | H332 | Harmful if inhaled |
| Carcinogenicity | 2 | H351 | Suspected of causing cancer if inhaled |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1A | H360FD | May damage fertility. May damage the unborn child |
| Reproductive Toxicity, Effects On or Via Lactation | H362 | May cause harm to breast-fed children | |
| Acute Oral Toxicity | 4 | H302 | Harmful if swallowed |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1B | H360 | May damage fertility or the unborn child |
Side Effects
SIDER: Haemorrhage, vulvovaginitis, amenorrhoea, abdominal pain, fatigue, nausea, menometrorrhagia, abdominal pain lower, asthenia, ovarian cyst, dizziness, breast tenderness, headache, seborrhoeic dermatitis.
AHFS: Reported in 5% or more of women: abdominal pain, leukorrhea, headache, vaginitis, back pain, breast pain, acne, depression, hypertension, upper respiratory infection, nausea, nervousness, dysmenorrhea, weight increase, skin disorder, decreased libido, abnormal Pap smear, sinusitis.
Mutagenicity
Levonorgestrel was not found to be mutagenic or genotoxic in the Ames Assay, in vitro mammalian culture assays utilizing mouse lymphoma cells and Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in an in vivo micronucleus assay in mice.
References
- Levonorgestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- Lang, R.; Reimann, R. Studies for a Genotoxic Potential of Some Endogenous and Exogenous Sex Steroids. I. Communication: Examination for the Induction of Gene Mutations Using the Ames Salmonella/microsome Test and the HGPRT Test in V79 Cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1993, 21 (3), 272–304. (View all citations for this reference)
LD50
- rat oral: 5010 mg/kg
- rat intraperitoneal: 11,200 mg/kg
- mouse intraperitoneal: 7300 mg/kg
- mouse oral: 5010 mg/kg
References
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference) - PubChem: Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
Biochemistry & Pharmacology
Progesterone Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
Androgen Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kumar, N.; Fagart, J.; Liere, P.; Mitchell, S. J.; Knibb, A. R.; Petit-Topin, I.; Rame, M.; El-Etr, M.; Schumacher, M.; Lambert, J. J.; Rafestin-Oblin, M. E.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Nestorone(R) as a Novel Progestin for Nonoral Contraception: Structure-Activity Relationships and Brain Metabolism Studies. Endocrinology 2017, 158 (1), 170-182. (View all citations for this reference)
- Kuhl, H., Pharmacology of estrogens and progestogens: influence of different routes of administration. Climacteric 2005, 8 Suppl 1, 3-63. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Estrogen Receptor Activity
Antagonist
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- Bartsch, V., Gynaecological uses of dienogest alone and in combination with oestrogens. Journal of Medical Drug Reviews 2015, 5, 1-31. (View all citations for this reference)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity
Conflicting reports: not active (Ruan, Lello), weakly effective (Nath), active (Bartsch), binds to GR (Jordan), low affinity (Africander)
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Nath, A.; Sitruk-Ware, R., Different cardiovascular effects of progestins according to structure and activity. Climacteric 2009, 12, 96-101. (View all citations for this reference)
- Jordan A. Toxicology of progestogens of implantable contraceptives for women. Contraception. 2002; 65:3-8. (View all citations for this reference)
- Bartsch, V., Gynaecological uses of dienogest alone and in combination with oestrogens. Journal of Medical Drug Reviews 2015, 5, 1-31. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activity
Agonist with high relative binding affinity. Conflicting reports on antagonism: Ruan and Lello indicate not active, while Africander says some anti-mineralocorticoid activity in rat models.
References
- Africander, D.; Verhoog, N.; Hapgood, J. P., Molecular mechanisms of steroid receptor-mediated actions by synthetic progestins used in HRT and contraception. Steroids 2011, 76 (7), 636-52. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
Target Pathways
Bioavailability
100%
References
- Levonorgestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolism
CYP3A4
Apparent Volume of Distribution
260 L (Healthy female volunteers under fasting conditions)
1.8 L/kg
References
- Levonorgestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Cmax
14.1 +/- 7.7 ng/mL (adult females, single dose of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel] administered in the morning
7.5 +/- 3.8 ng/mL (adolescent females, single dose of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel] administered in the evening)
Tmax
1.6 +/- 0.7 h (adult females, single dose of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel] administered in the morning
1.5 +/- 0.7 h (adolescent females, single dose of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel] administered in the evening)
Elimination Half-Life (t1/2)
36 +/- 13 h at steady-state (Toxnet)
28 +/- 6.4 h (Toxnet)
24.4 +/- 5.3 h (adult females, one table of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel])
22.2 +/- 6.8 h (adolescent females, one table of Plan B [0.75 mg levonorgestrel])
Serum Protein Binding
47.5% bound to SHBG, 50% to serum albumin, 2.5% unbound
References
- Schindler, A. E.; Campagnoli, C.; Druckmann, R.; Huber, J.; Pasqualini, J. R.; Schweppe, K. W.; Thijssen, J. H. H., Classification and pharmacology of progestins. Maturitas 2003, 46, 7-16. (View all citations for this reference)
- Plan B Drug Approval Package (View all citations for this reference)
Excretion
45% of LNG and metabolites excreted in the urine and 32% excreted in feces, mostly as glucuronide conjugates
References
- Levonorgestrel. Toxicology Data Network. US National Library of Medicine [Online Database] (View all citations for this reference)
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Clearance
7.7 +/- 2.7 L/h (Healthy female volunteers under fasting conditions)
References
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Enzyme Interactions
Inhibits 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase 1, CYP19A1
Inhibition of Ovulation
0.05-0.1 mg/day
References
- Rebar, R. W.; Zeserson, K., CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NEW PROGESTOGENS IN COMBINATION ORAL-CONTRACEPTIVES. Contraception 1991, 44 (1), 1-10. (View all citations for this reference)
Transformation of Endometrium
5-6 mg/cycle
References
- Rebar, R. W.; Zeserson, K., CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NEW PROGESTOGENS IN COMBINATION ORAL-CONTRACEPTIVES. Contraception 1991, 44 (1), 1-10. (View all citations for this reference)
Menstrual Delay
0.25-1.0 mg/day
References
- Rebar, R. W.; Zeserson, K., CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NEW PROGESTOGENS IN COMBINATION ORAL-CONTRACEPTIVES. Contraception 1991, 44 (1), 1-10. (View all citations for this reference)
Indications
For the treatment of menopausal and postmenopausal disorders and alone or in combination with other hormones as an oral contraceptive.
References
- DrugBank: Levonorgestrel
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference) - PubChem: Levonorgestrel. (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolites
Name
Structure
Notes
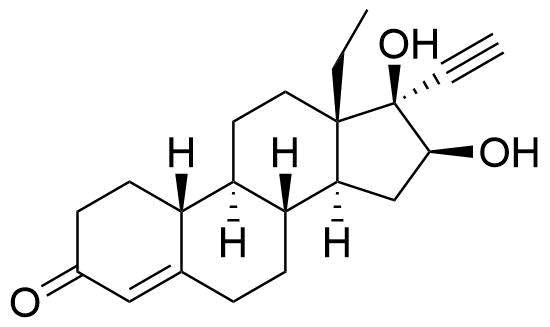
Sulfate conjugate also present, as well as the sulfate conjugate of the 16α stereoisomer. Metabolite of both levonorgestrel and norgestrel.
Impurities
Name
Structure
CASRN
Other Names & Identifiers
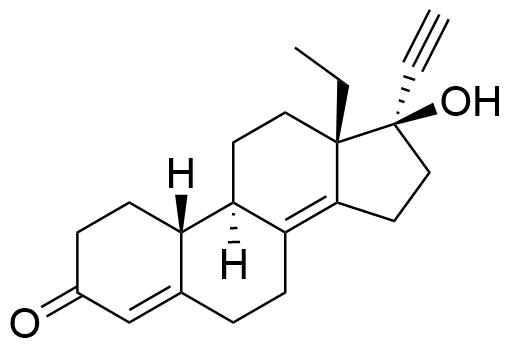
1260525-53-8
- BP Levonorgestrel Impurity A
- δ8(14)-levonorgestrel
- 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregna-4,8(14)-dien-20-yn-3-one
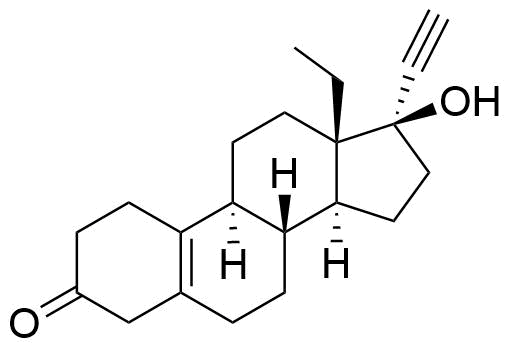
19914-67-1
- BP Levonorgestrel Impurity B
- 13-ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-5(10)-en-20-yn-3-one
US FDA-Approved Products
Name
Formulation
Status
ANDA #
Prescription
206851
WHO Essential Medicines
Name
Formulation
Tablet
LEVONORGESTREL: 1 mg
Tablet
LEVONORGESTREL: 150 μg
Tablet
WHO Prequalified Medicines
WHO Reference #
Name
Applicant
Formulation
LEVONORGESTREL: 0.15 mg
Tablet
Placebo tablet: 0 mg
LEVONORGESTREL: 0.15 mg
Tablet
Placebo Tablet: 0 mg