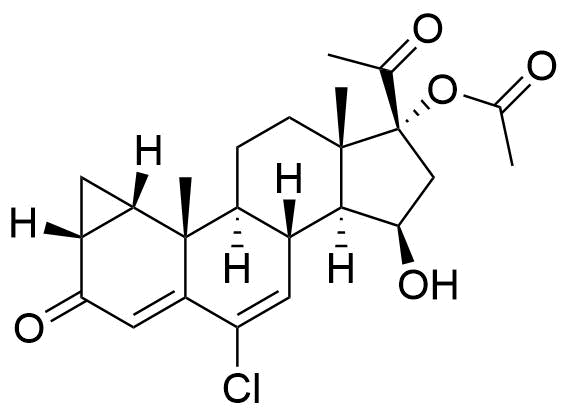
Cyproterone Acetate
Cyproterone Acetate (CPA) is a steroidal progestogen and potent antiandrogen. It is used in oral contraceptives, as a component of hormone therapy, and in the treatment of certain medical conditions, particularly androgen-related issues.
Tags
Identifiers
Abbreviation
CPA
References
Names
6-chloro-3,20-dioxo-1β,2β-dihydro-3'H-cyclopropa[1,2]pregna-1,4,6-trien-17-yl acetate
References
- BP 2017: Cyproterone Acetate monograph. (View all citations for this reference)
CASRN
427-51-0
References
PubChem CID
9880
ECHA InfoCard
- 100.006.409
- EC / List #: 207-048-3
IUPHAR/BPS
2865
DrugBank Accession Number
DB04839
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
UNII
4KM2BN5JHF
KEGG Entry Number
D01368
ChEBI ID
CHEBI:50743
ChEMBL ID
CHEMBL139835
ChemSpider ID
9496
PDB
CA4
ATC Code(s)
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Physical & Chemical Properties
Molecular Formula
C24H29ClO4
References
Molecular Weight
416.9 g/mol
References
Appearance
White or almost white crystalline powder
References
- BP 2017: Cyproterone Acetate monograph. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Melting Point
BP: About 210 °C
DrugBank, IARC, Toxnet: 200-201 °C
References
- BP 2017: Cyproterone Acetate monograph. (View all citations for this reference)
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference) - WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
- Toxnet: Cyproterone Acetate (View all citations for this reference)
Solubility
Practically insoluble in water, very soluble in methylene chloride, freely soluble in acetone, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in anhydrous ethanol
References
- BP 2017: Cyproterone Acetate monograph. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Specific Optical Rotation
+152 to +157, 0.25 g dried substance in acetone, dilute to 25.0 mL
References
- BP 2017: Cyproterone Acetate monograph. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Storage Conditions
Store in a tightly closed container in a dry, ventilated location, recommended at 2-8 °C. Do not store above 25 °C.
Toxicology
GHS Hazard Code(s)
| Class | Category | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Dermal Toxicity | 4 | H312 | Harmful in contact with skin |
| Acute Inhalation Toxicity | 4 | H332 | Harmful if inhaled |
| Carcinogenicity | 2 | H351 | Suspected of causing cancer if inhaled |
| Reproductive Toxicity | 1A | H360FD | May damage fertility. May damage the unborn child |
| Specific Target Organ Toxicity, Repeated Exposure | 2 | H373 | Causes damage to organs through prolonged or repeated exposure |
Mutagenicity
Not found to be mutagenic in the Ames Salmonella/microsome direct plate incorporation protocol.
References
- Lang, R.; Reimann, R. Studies for a Genotoxic Potential of Some Endogenous and Exogenous Sex Steroids. I. Communication: Examination for the Induction of Gene Mutations Using the Ames Salmonella/microsome Test and the HGPRT Test in V79 Cells. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1993, 21 (3), 272–304. (View all citations for this reference)
Genotoxicity
Reports vary. Siddique et al. found CPA to be genotoxic to human lymphocytes at 20 and 30 μm using chromosomal aberrations, mitotic index, and sister chromatid exchanges. Reimann et al. did not find CPA to be genotoxic in human lymphocyte assay in vitro and mouse bone marrow micronucleus test in vivo.
References
- Toxnet: Cyproterone Acetate (View all citations for this reference)
- Siddique, Y. H.; Afzal, M. Genotoxic Potential of Cyproterone Acetate: A Possible Role of Reactive Oxygen Species. Toxicol. Vitr. 2005, 19 (1), 63–68. (View all citations for this reference)
- (1) Reimann, R.; Kalweit, S.; Lang, R. Studies for a Genotoxic Potential of Some Endogenous and Exogenous Sex Steroids. II. Communication: Examination for the Induction of Cytogenetic Damage Using the Chromosomal Aberration Assay on Human Lymphocytes in Vitro and the Mouse Bone Marrow Micronucleus Test in vivo. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 1996, 28 (2), 133–144. (View all citations for this reference)
LD50
rat intraperitoneal: 565 mg/kg
mouse intraperitoneal: 3300 mg/kg
TD50
mouse: 21.9 mg/kg/day
Biochemistry & Pharmacology
Progesterone Receptor Activity
Agonist
Androgen Receptor Activity
Potent antagonist
References
- Stanczyk, F. Z.; Archer, D. F.; Bhavnani, B. R., Ethinyl estradiol and 17 beta-estradiol in combined oral contraceptives: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and risk assessment. Contraception 2013, 87 (6), 706-727. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
- KEGG: Cyproterone Acetate (View all citations for this reference)
- Krattenmacher, R. Drospirenone: Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics of a Unique Progestogen. Contraception 2000, 62 (1), 29–38. (View all citations for this reference)
Estrogen Receptor Activity
Antagonist
References
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Glucocorticoid Receptor Activity
Agonist
References
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activity
No activity
References
- WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer: IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Volume 91: Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Contraceptives and Combined Estrogen-Progestogen Menopausal Therapy. 2007, Lyon, France. (View all citations for this reference)
- Hapgood, J. P.; Africander, D.; Louw, R.; Ray, R. M.; Rohwer, J. M., Potency of progestogens used in hormonal therapy: toward understanding differential actions. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 2013, 142, 39-47. (View all citations for this reference)
- Ruan, X.; Seeger, H.; Mueck, A. O., The pharmacology of nomegestrol acetate. Maturitas 2012, 71 (4), 345-53. (View all citations for this reference)
- Lello, S., Nomegestrol Acetate Pharmacology, Safety Profile and Therapeutic Efficacy. Drugs 2010, 70 (5), 541-559. (View all citations for this reference)
- Krattenmacher, R. Drospirenone: Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics of a Unique Progestogen. Contraception 2000, 62 (1), 29–38. (View all citations for this reference)
Bioavailability
88%
Elimination Half-Life (t1/2)
Drugbank: 38 h (oral), 96 h (intramuscular)
Toxnet: 43.9 +/- 12.8 h from two 50 mg CPA tablets
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference) - Toxnet: Cyproterone Acetate (View all citations for this reference)
Serum Protein Binding
Almost exclusively bound to albumin. 3.5-4% unbound.
Metabolism
Metabolized by CYP3A4
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Excretion
60% in the bile and 33% through kidneys.
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Cmax
285 ng/mL from two 50 mg CPA tablets
Enzyme Interactions
Inhibits CYP19A1, CYP2D6 (DrugBank). May inhibit CYP2C8 (Toxnet).
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Indications
Advanced prostate carcinoma, metastatic hormone refractory prostate cancer, paraphilia, severe acne.
References
- DrugBank: Cyproterone Acetate
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ, Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, Assempour N, Iynkkaran I, Liu Y, Maciejewski A, Gale N, Wilson A, Chin L, Cummings R, Le D, Pon A, Knox C, Wilson M. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1037 (View all citations for this reference)
Metabolites
Name
Structure
Notes
Impurities
Name
Structure
CASRN
Other Names & Identifiers
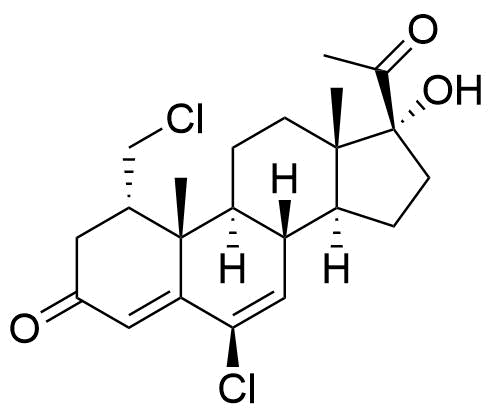
- BP Cyproterone Tablets Impurity 2
- 17α-Hydroxy-6-chloro-1α-chloromethylpregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione
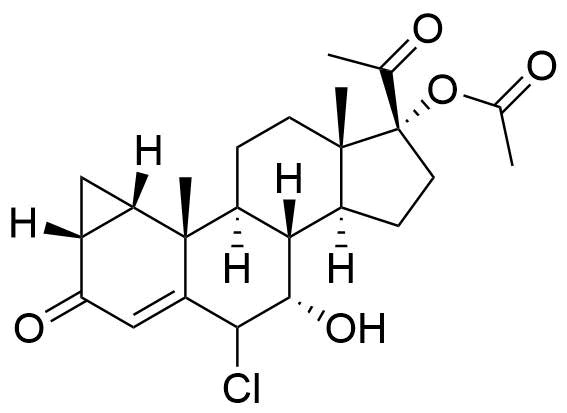
- BP CPA Impurity G
- BP Cyproterone Tablets Impurity 1
- 6β-Chloro-7α,17α-dihydroxy-1α,2α-methylenepregna-4-ene-3,20-dione
- 6β-Chloro-7α-hydroxy-3,20-dioxo-1β,2β-dihydro-3'H-cyclopropa[1,2]pregna-1,4-dien-17-yl Acetate
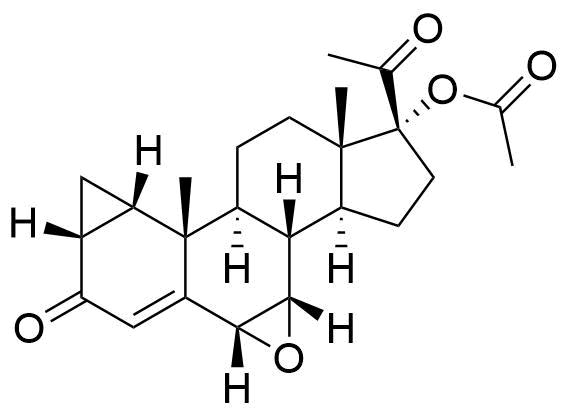
- BP CPA Impurity J